Key concepts for Jitterbit API Manager
This page covers the fundamental concepts you need to understand when working with Jitterbit API Manager, including API types, security features enforced through API gateways, and service URL structure.
API types
You can create and publish three types of APIs in API Manager. Each type interacts with Harmony uniquely within the system architecture.
For more information on Jitterbit security and system architecture, see Jitterbit security and architecture white paper.
Custom API
Custom APIs expose a Harmony operation for consumption. To configure a custom API, you must first create and deploy an operation to Harmony. The operation can be any Studio or Design Studio operation. When you configure the custom API, you reference the existing operation. API consumers call and consume the operation through the custom API. Custom APIs route through Jitterbit agents (either cloud agent groups or private agents).
How custom APIs work
When an API consumer calls a custom API, the following process occurs:
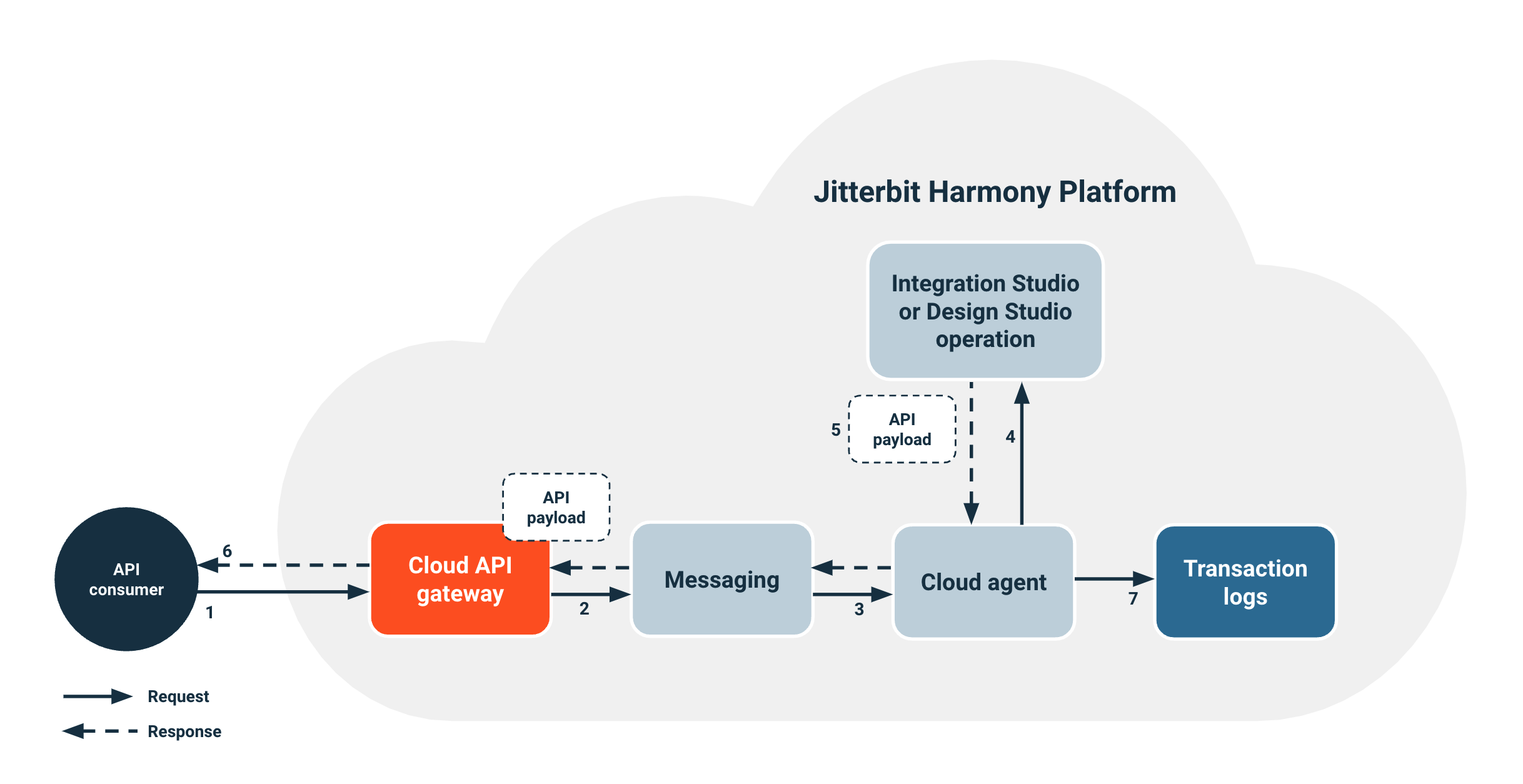
- An API consumer makes a call to the custom API at the cloud API gateway.
- The cloud API gateway authenticates the request and enforces security policies. Then it routes the custom API request to the messaging service, which routes requests for agent groups.
- A cloud agent receives the request from the messaging service.
- The cloud agent references the custom API operation that you specified during custom API configuration and triggers the deployed operation.
- The operation responds with an API payload. This payload is consistent with the response type that you selected during custom API configuration.
- The cloud agent routes the API payload back to the API consumer.
Note
Keep the following considerations in mind when working with custom APIs:
-
The API payload remains on the agent for only two days. This applies unless the operation uses Temporary Storage.
-
The system sends runtime status information and logs of running operations to the transaction logs database.
-
Consumer data isn't stored in the transaction logs database unless you enable debug mode during custom API configuration.
For information on configuring a custom API, see Custom API configuration.
OData service
OData services expose a Design Studio API entity operation for consumption. To configure an OData service, you must first create and deploy an API entity operation to Harmony. When you configure the OData service, you reference the existing API entity operation. API consumers call and consume the operation through the OData service. OData services route through Jitterbit agents (either cloud agent groups or private agents).
How OData services work
When an API consumer calls an OData service, the following process occurs:
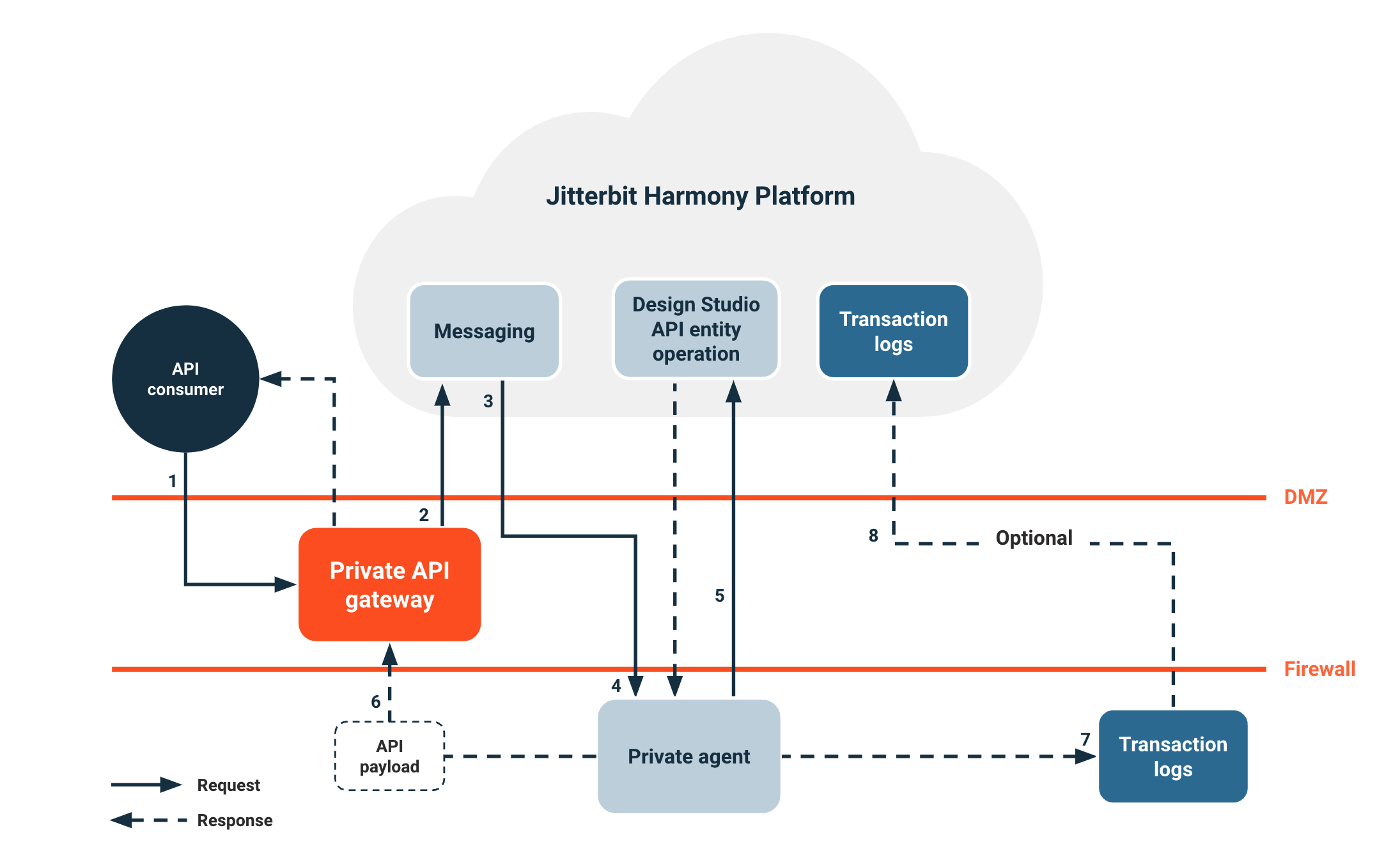
- An API consumer makes a call to the OData service at the private API gateway.
- The private API gateway authenticates the request and enforces security policies. Then it routes the OData service request.
- The messaging service receives the request and routes requests for agent groups.
- The private agent receives the request from the messaging service.
- The private agent references the OData service API entity operation in Harmony and triggers the deployed entity operation.
- The private agent routes the API payload from the operation response through the private API gateway back to the API consumer.
Note
Keep the following considerations in mind when working with OData services:
- The API payload remains on the agent for only two days. This applies unless the operation uses Temporary Storage.
- The system sends runtime status information and logs of running operations to the transaction logs database on the private agent.
- Consumer data isn't stored in the transaction logs database unless you enable debug mode during OData service configuration.
- You can optionally sync logs on the private agent to the transaction logs database within Harmony.
For information on configuring an OData service, see OData service configuration.
Proxy API
Proxy APIs work with an existing third-party API and don't route through Jitterbit agents, unlike custom APIs or OData services that expose a Harmony operation for consumption. The API that you're proxying must be accessible to the gateway that processes the API, either the cloud API gateway or a private API gateway:
-
Cloud API gateway: If you use the API gateway that Jitterbit hosts on Harmony, the existing API must be publicly accessible, even if secured. The API that you're trying to proxy can't be behind a firewall. To allowlist the cloud API gateway IP addresses and allow the gateway access to the API that you're proxying, see Allowlist information and navigate to https://services.jitterbit for your region.
-
Private API gateway: If you use a private API gateway, the existing API must be accessible by the private API gateway.
How proxy APIs work
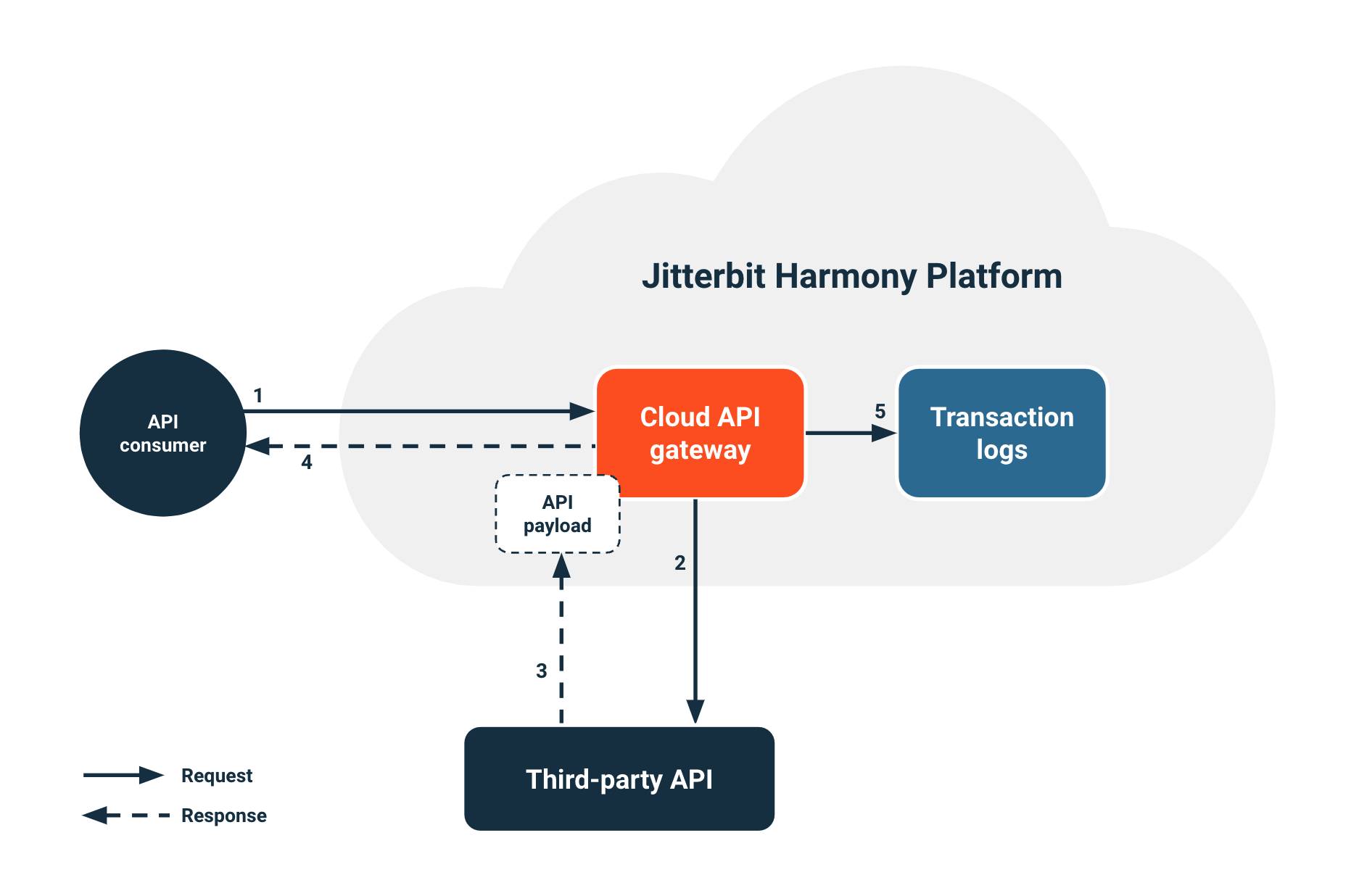
When an API consumer calls a proxy API, the following process occurs:
- An API consumer makes a call to the proxy API at the cloud API gateway.
- The cloud API gateway authenticates the request and enforces security policies. Then it routes the proxy API call and sends it to the third-party API that you're proxying.
- The third-party API responds with an API payload that routes to the cloud API gateway and back to the API consumer.
- The system sends runtime status information to the transaction logs database.
Note
Consumer data isn't stored in the transaction logs database unless you enable debug mode during proxy API configuration.
For information on configuring a proxy API, see Proxy API configuration.
API security
All API requests in Jitterbit API Manager must pass through API gateways, which serve as the primary security enforcement layer for authentication, authorization, and access control. API Manager provides multiple security features that you can configure and manage for various use cases. For information on security features within Jitterbit's system architecture, see Jitterbit security.
Security profiles
By default, an API is anonymous and publicly accessible when you create it, unless you configure a security profile in the API Manager Security Profiles page and assign it to the API.
An API security profile governs and secures API consumption. Security profiles allow a published API to be consumed only by a specific API consumer or a group of consumers. You can create and assign security profiles if you're an organization member with Admin permission.
Harmony organization administrators can require that you assign security profiles to each API when you create it by using a setting in the Harmony organization's policies.
Authentication types
Authentication options in security profiles control API access by API consumers. The following table shows the available security profile authentication types:
| Anonymous | Anonymous authentication allows the API to be publicly accessible without requiring any authentication. |
| Basic | Basic authentication uses HTTP authentication to provide API access. When using basic authentication, consumers include the username and password in an encoded string in the authorization header of each request made. |
| OAuth 2.0 | OAuth 2.0 authentication uses one of Microsoft Entra ID, Google, Okta, or Salesforce as the identity provider. When using OAuth 2.0 authentication, the consumer must validate their identity provider credentials to access an API at runtime. For more information on configuring an API identity provider, see API identity provider configuration. |
| API Key | API key authentication uses a key-value pair to access an API. |
Note
Security profiles are cached on the API gateway. Changes to the security profiles of an already-active API can take several minutes to take effect.
API gateways as security enforcement points
Both the cloud API gateway and private API gateways serve as security enforcement points in the API Manager architecture. At these gateways, the system performs the following actions:
- Authenticate API consumers using the assigned security profile
- Enforce rate limiting and IP address restrictions
- Apply SSL encryption requirements
- Log all API access for security auditing
- Block unauthorized requests before they reach backend systems
This security model ensures consistent protection across all API types. It also provides centralized control over API access policies.
Multiple security profiles
You can use multiple security profiles to employ different methods of authentication and security options in the same environment, with each profile targeting a specific group of API consumers.
For example, if you have two types of consumers (accounting and finance), and two APIs (API-Revenue and API-Budget) in an environment and API-Revenue is intended for accounting consumers and API-Budget is intended for both accounting and finance consumers, you can create a single security profile for accounting consumers and assign it to both APIs. You could then create a separate security profile for finance consumers and assign it to API-Budget.
The result of the two security profiles is that accounting consumers (using their security profile) can only access API-Revenue, and finance consumers (using their separate security profile) can access either API-Revenue or API-Budget.
These security profile combinations are allowed:
- You can assign multiple security profiles with basic authentication to a single API.
- You can assign multiple security profiles with API key authentication to a single API.
- You can assign a combination of security profiles that use basic and API key authentication to a single API.
Any other security profile combination isn't allowed.
Rate limits
Each organization has two allowances, as stated in the organization's Jitterbit license agreement. API gateways enforce these limits at the point of entry:
-
API hits per month allowance: The total allowance provided to an organization in a month. All calls received by all APIs (in all environments) in a single month count toward this limit.
-
API hits per minute allowance: The maximum rate at which an organization's allowance can be consumed.
By default, an environment or security profile can access an organization's total allowance for hits across all APIs within a minute.
After an organization uses up its hits per month allowance, all APIs within the organization receive an Error 429 until the allowance resets to their max allowance on the first day of the following month.
You can use rate limits at the environment and security profile level to enforce a shared maximum number of API hits per minute that can be made across all APIs within an environment to which a security profile is assigned.
Note
The system enforces rate limiting at the organization level, environment level, and security profile level. It doesn't enforce rate limiting at the API level.
Trusted IP ranges
By default, a security profile doesn't limit access to any predetermined range of IP addresses. You can limit access to the APIs within a security profile to consumers from a single IP address or a range of IP addresses during security profile configuration.
When a consumer attempts to access an API with a security profile that's limited to a certain IP address or range, the API gateway checks the consumer's IP address against the allowed ranges. IP addresses that don't meet the criteria are rejected and an Error 429 message is returned.
SSL-only mode
You can configure any API to use SSL encryption. By default, every API supports both HTTP and HTTPS transfer.
The SSL-only option lets you forward HTTP traffic to ensure all communication is encrypted. The identity of the HTTPS URL is verified by Symantec Class 3 Secure Server SHA256 SSL CA. The connection to the HTTPS URL is encrypted with modern cryptography.
You can enable the SSL-only option during the configuration of a custom API, OData service, or proxy API.
API logs
For every hit on an API, the security profile used to access the API is recorded in a log. The API Logs page displays a table of all API processing logs and debug logs (if debug logging is enabled) to help publishers and consumers troubleshoot related issues. Logs display for custom, OData service, and proxy APIs when they're called through the cloud API gateway or a private API gateway.
API service URLs
You access custom APIs, OData services, and proxy APIs that are created through Jitterbit API Manager by using an API's service URL. The service URL is the URL used to consume the API using the configured authentication method.
You can call the service URL from an application. If the API supports GET, you can paste the URL into a web browser to consume the API manually.
Service URL format
All API service URLs follow the same format. Proxy APIs may have additional service path parameters:
<Protocol>://<Base URL>/<Environment URL Prefix>/<Version>/<Service Root>
<Protocol>://<Base URL>/<Environment URL Prefix>/<Version>/<Service Root>/<Service Path>
Example
These are typical examples of an API's service URL:
- Custom API or OData service:
https://JBExample123456.jitterbit.net/Development/1/customer - Proxy API:
https://JBExample123456.jitterbit.net/Development/1/dog/pet/{petId}/uploadImage
Note
API service URLs have a maximum length limit of 8,000 characters. Ensure your URL components (including service paths for proxy APIs) stay within this limit to avoid request failures. When exceeded, the API gateway returns an HTTP error 414 (URI Too Large).
Service URL components
Each API's service URL is automatically constructed of these parts:
| Part | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | https |
The protocol is always https |
| Base URL | JBExample123456.jitterbit.net |
The base URL. The default base URL consists of the Harmony organization name, Harmony organization ID, and Harmony region domain name. To use a custom domain name as the base URL for your published APIs, you can use custom domain configuration methods |
| Harmony organization name | JBExample |
The name of the Harmony organization. For trial licenses that were initiated before certain dates, specific naming conventions may apply |
| Harmony organization ID | 123456 |
The unique identifier for the Harmony organization |
| Region domain | jitterbit.net |
The Harmony region domain name of the Harmony organization: • APAC: jitterbit.cc• EMEA: jitterbit.eu• NA: jitterbit.net |
| Environment URL prefix | Development |
The URL prefix in Environments |
| Version | 1 |
The version that you specify in the configuration of the custom API, OData service, or proxy API |
| Service root | customer, dog |
The service root that you specify in the configuration of the custom API, OData service, or proxy API |
| Service path | pet/{petId}/uploadImage |
The path that you specify in the configuration of the proxy API (proxy APIs only) |