Hochverfügbarkeitsbereitstellung in AWS für Jitterbit App Builder
Einführung
Sie können die folgenden AWS-Produkte verwenden, um eine hochverfügbare (HA) App Builder-Umgebung zu erstellen:
-
Ein S3-Bucket, konfiguriert mit Lese-/Schreibzugriff für App Builder, um Sicherheitskeys zu erstellen und zu teilen.
-
Eine RDS auf EC2-Instanz für die App Builder-Datenbank.
-
ElastiCache, das als Nachrichtenbus für den Informationsaustausch zwischen App Builder-Instanzen verwendet wird.
-
(Optional) Elastic Beanstalk kann verwendet werden, um App Builder-Instanzen zu verwalten und einen Lastenausgleich bereitzustellen, um Clientanfragen zu verteilen.
Das folgende Diagramm zeigt eine Möglichkeit, wie diese Dienste als App Builder-Umgebung genutzt werden können:
load balancer] W[fa:fa-globe Web browser] AB1[fa:fa-window-restore App Builder] AB2[fa:fa-window-restore App Builder] AB3[fa:fa-window-restore App Builder] KS@{shape: das, label: "fa:fa-key S3
key storage"} MB["fa:fa-random Message bus
(Redis)"] ABDB[(fa:fa-database App Builder
database)] ODS@{ shape: lin-cyl, label: "fa:fa-table Other
data sources" } A --> B W --> B subgraph Process_Group [Elastic Beanstalk] B --> AB1 B --> AB2 B --> AB3 end AB1 --> MB AB2 --> MB AB3 --> MB subgraph EC[ElastiCache] MB end MB --> ABDB MB --> ODS KS -.- AB1 KS -.- AB2 KS -.- AB3
Speicherung von Datenverschlüsselungsschlüsseln in einem S3
Wie in der Datenverschlüsselungskonfiguration erwähnt, kann der lokale Speicher der EC2-Instanz nicht für die langfristige Speicherung verwendet werden. Folglich müssen Datenverschlüsselungsschlüssel (DEKs) in S3-Buckets gespeichert werden, gemäß den folgenden Details:
- Bucket:
vinyl-data-encryption-keys(Standard-S3-Bucket, der von Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebungen verwendet wird.) - Adresse:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/vinyl-data-encryption-keys - Zugriff:
aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-role
Innerhalb des Buckets sind DEKs mit dem Namen der Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebung vorangestellt.
Konfigurieren der Speicherung von Datenverschlüsselungsschlüsseln (DEK) in der Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebung
App Builder wird mit einem .ebextensions-Skript geliefert, das die Umgebungsparameter für die DEK-Speicherung registriert. Diese Parameter umfassen Folgendes:
| Eigenschaft | Standard | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
DataEncryptionKeyStorage |
S3 | S3 |
DataEncryptionKeyS3BucketEndpoint |
https://{bucket}.s3{-aws-region}.amazonaws.com |
https://s3.amazonaws.com/vinyl-data-encryption-keys |
DataEncryptionKeyS3KeyPrefix |
{elastic-beanstalk-environment-name} |
abacceptance |
App Builder wird nicht mit den Standardumgebungseigenschaften von Elastic Beanstalk gestartet. Sie müssen die Werte für DataEncryptionKeyS3BucketEndpoint und DataEncryptionKeyS3KeyPrefix ändern.
Gewähren Sie Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebungen Zugriff auf S3-Buckets
EC2-Instanzen innerhalb einer Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebung sind einer Rolle zugewiesen. Die folgende Beispielrichtlinie gewährt Zugriff auf einen S3-Bucket:
{
"Version": "2025-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::{bucket-name}/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
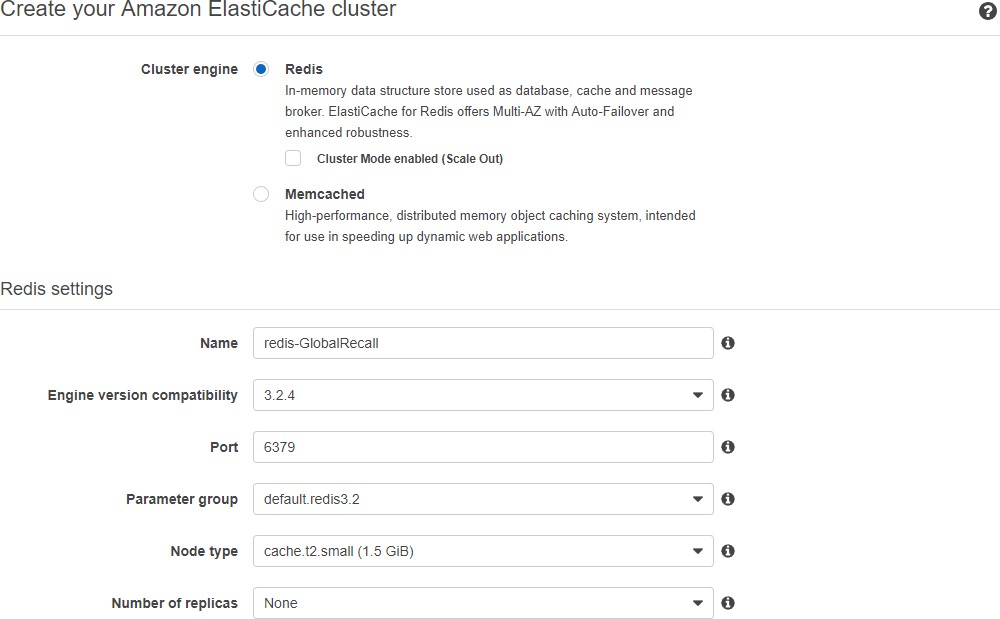
ElastiCache-Setup
Sie können ElastiCache verwenden, um zwischen App Builder-Servern zu kommunizieren. Ein kleiner Knoten, ohne Replikate oder Shards, ist ausreichend.
Verwenden Sie die folgenden Informationen, wenn Sie die Anwendungsserver in den Beanstalk-Konfigurationen einrichten:
Datenbank-Setup
Das Datenbank-Setup liegt außerhalb des Umfangs dieses Dokuments. Jitterbit kann auf Wunsch Anweisungen zur RDS-Einrichtung bereitstellen.
Elastic Beanstalk-Setup
Um einen AWS Elastic Beanstalk-Dienst einzurichten, befolgen Sie diese Schritte:
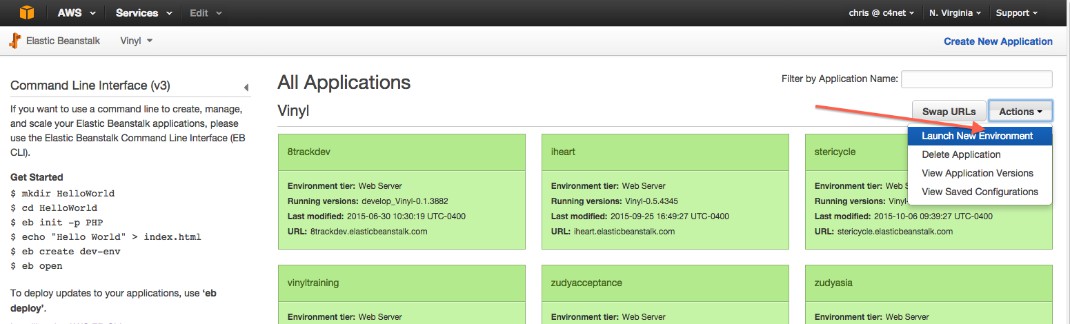
-
Erstellen Sie die Umgebung:
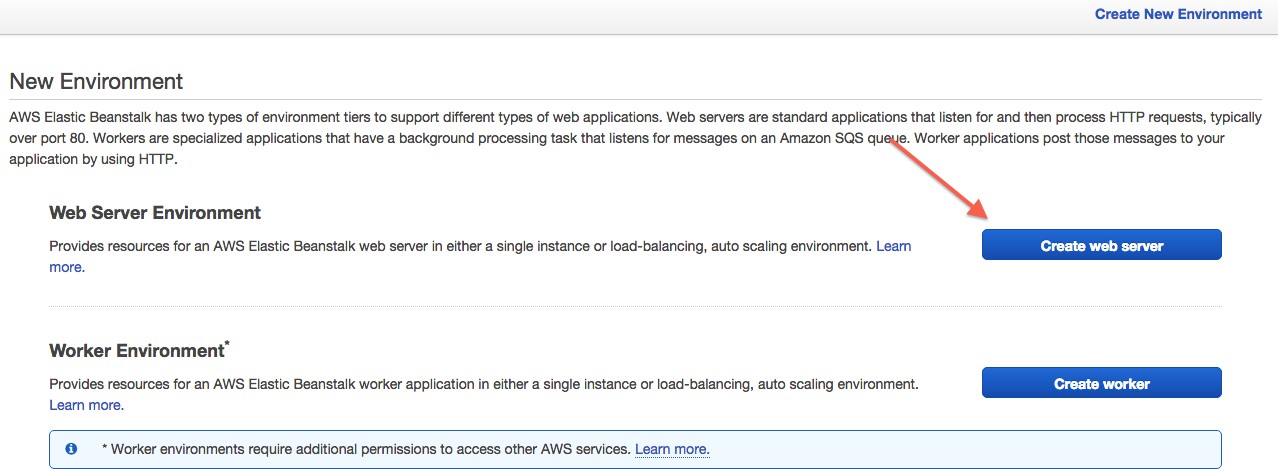
-
Wählen Sie Webserver erstellen:
-
Wählen Sie IIS:
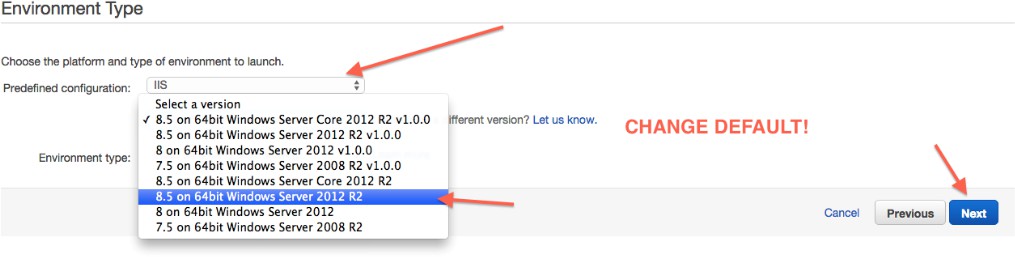
Um die Standardwerte zu ändern, wählen Sie Plattformversion ändern, und wählen Sie dann 8.5 auf 64-Bit Windows Server 2012 R2:
-
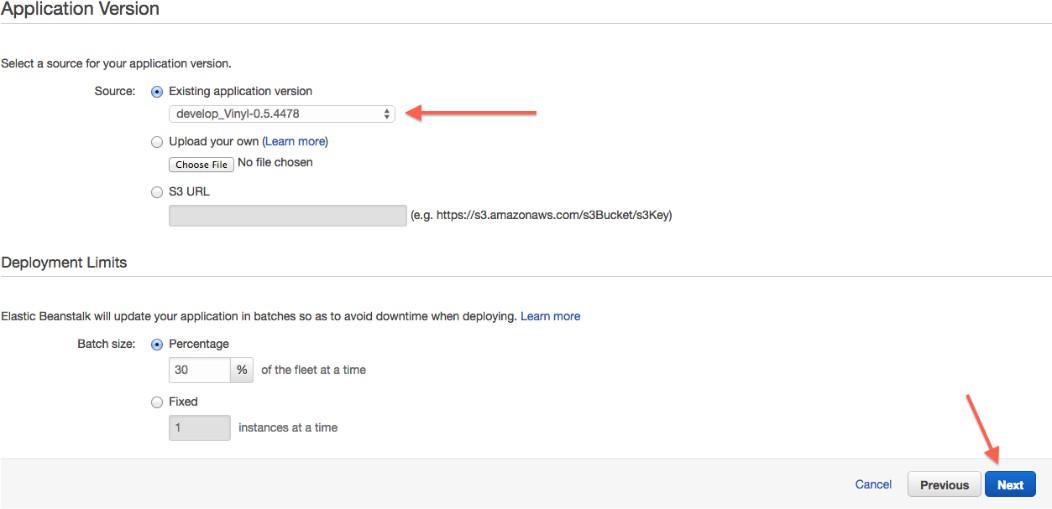
Wählen Sie die entsprechende Anwendungsversion:
-
Geben Sie den Umgebungsnamen ein. Dies wird Teil einer URL, die verwendet werden kann, um auf diese Umgebung zuzugreifen:
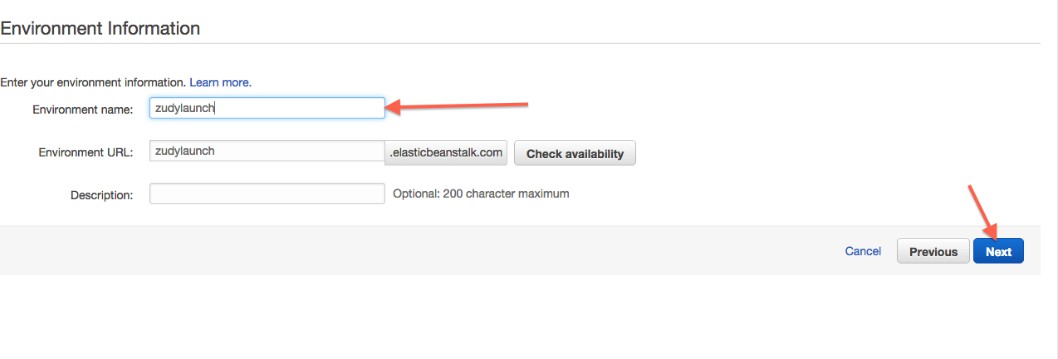
Tipp
Dieser Namensraum wird in allen Elastic Beanstalk-Instanzen für alle AWS-Kunden verwendet.
-
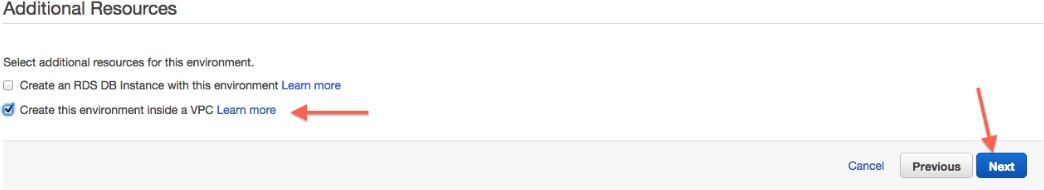
Aktivieren Sie Diese Umgebung innerhalb eines VPC erstellen:
-
Setzen Sie die folgenden Werte:
- Instanztyp: t2.small (Jitterbit empfiehlt
T2.smallundT2.mediumInstanzen für Entwicklungs- und QA-Zwecke sowie größere Instanzen für Produktionsumgebungen.) - EC2-Schlüsselpaar: vinyl
- (Optional) Geben Sie Ihre Email-Adresse ein, um über Umgebungsprobleme informiert zu werden.
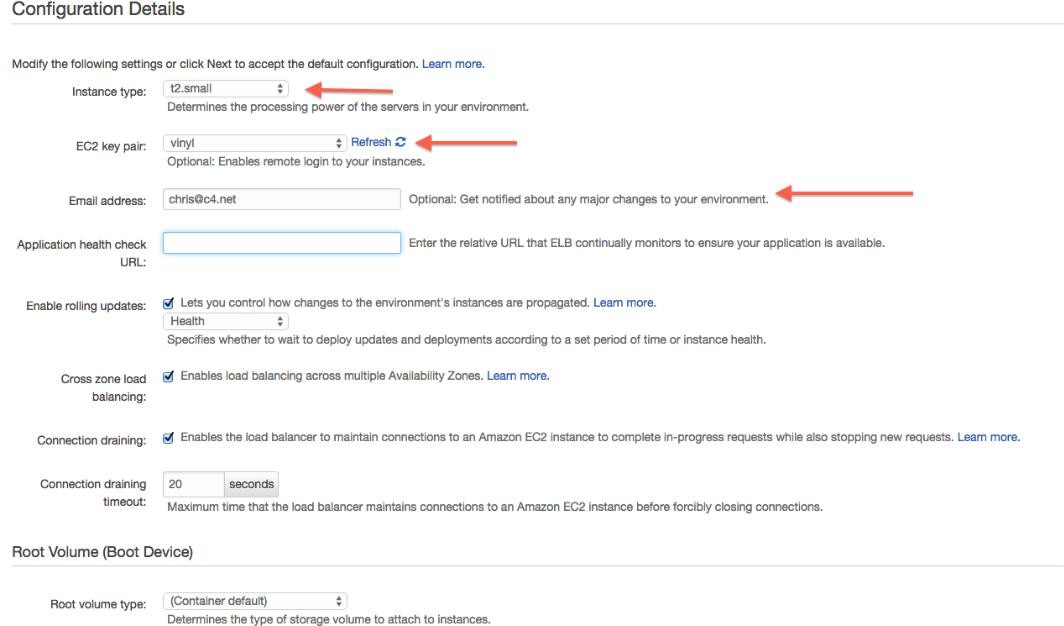
- Instanztyp: t2.small (Jitterbit empfiehlt
-
Konfigurieren Sie die VPC-Einstellungen entsprechend. (Die Sichtbarkeit des ELB sollte Extern sein.)
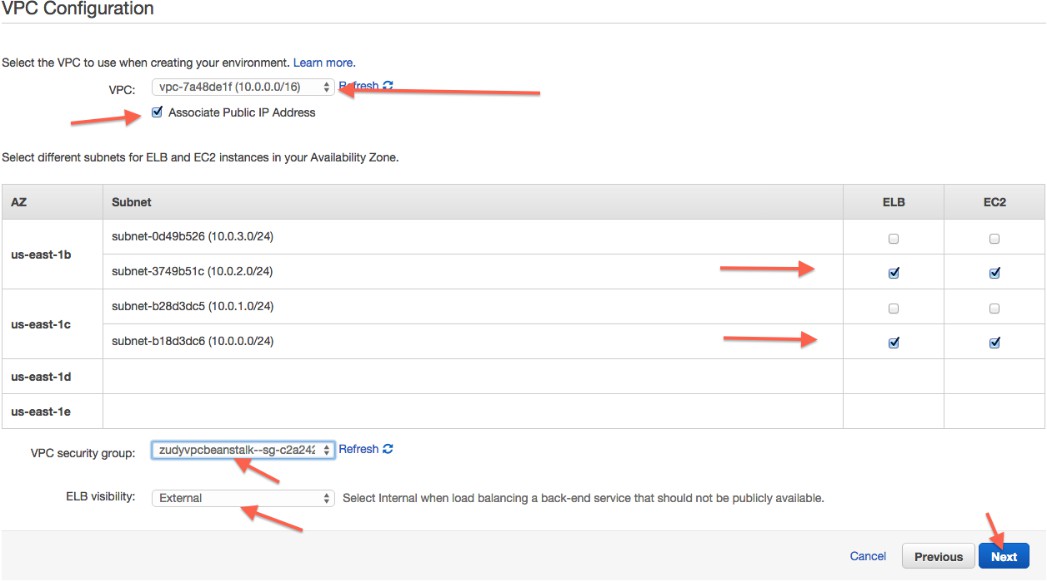
-
Überprüfen Sie die Zusammenfassung:
-
Setzen Sie die Berechtigungen:
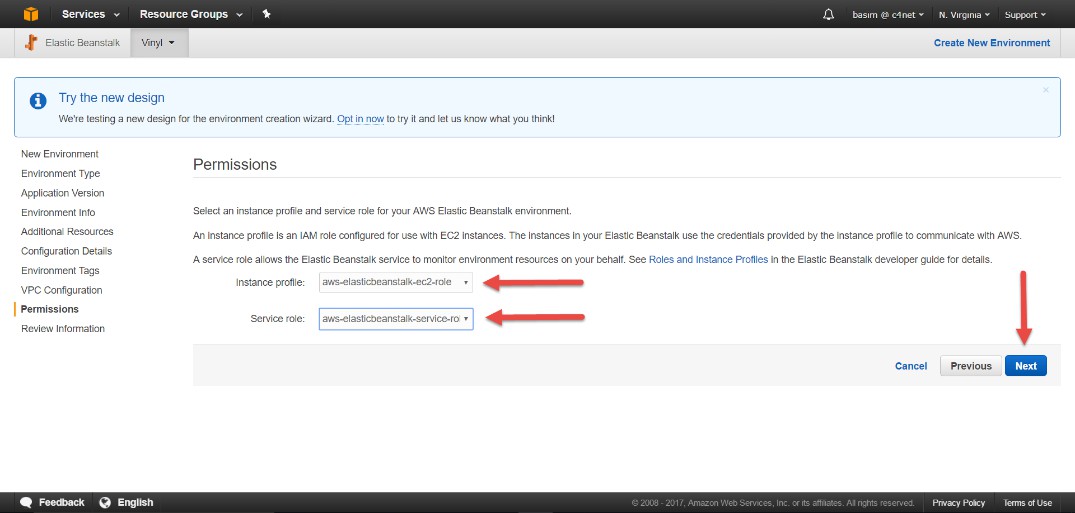
-
Speichern Sie die Konfiguration:
Nachdem die Umgebung bereit ist
Nachdem die Umgebung im Dashboard grün erscheint, müssen einige zusätzliche Parameter konfiguriert werden. Unter Konfiguration > Softwarekonfiguration setzen Sie Werte für die folgenden Verbindungsinformationen Felder:
-
ConnectionInfo:Datenbanktyp
-
ConnectionInfo:HostName
-
ConnectionInfo:Datenbankname
-
ConnectionInfo:Benutzername
-
ConnectionInfo:Passwort
Nachdem Sie diese Felder ausgefüllt haben, öffnet sich der App Builder. (Weitere Schritte für eine Datenbankinstallation oder -aktualisierung können erforderlich sein.)
Konfigurieren von HTTPS
Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebungen beenden die HTTPS-Verbindung am Elastic Load Balancer. Die Unterstützung von Reverse-Proxys durch den App Builder ermöglicht es, dieses Szenario zu erkennen und zu handhaben. Der App Builder erkennt drei Umgebungsvariablen, die beim Bereitstellen der Elastic Beanstalk-Instanz definiert werden. Diese Umgebungsvariablen sind skriptgesteuert; Sie müssen sie nicht selbst konfigurieren.
HTTPS wird für alle neuen Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebungen dringend empfohlen. Standardmäßig sind jedoch neue Elastic Beanstalk-Umgebungen nicht für HTTPS konfiguriert. Um Elastic Beanstalk so zu konfigurieren, dass HTTPS-Anfragen akzeptiert werden, befolgen Sie diese Schritte:
-
Melden Sie sich bei der Amazon Web Services-Konsole an.
-
Wählen Sie unter Dienste Elastic Beanstalk.
-
Wählen Sie die Umgebung aus, die Sie aktualisieren.
-
Wählen Sie Konfiguration im linken Menü.
-
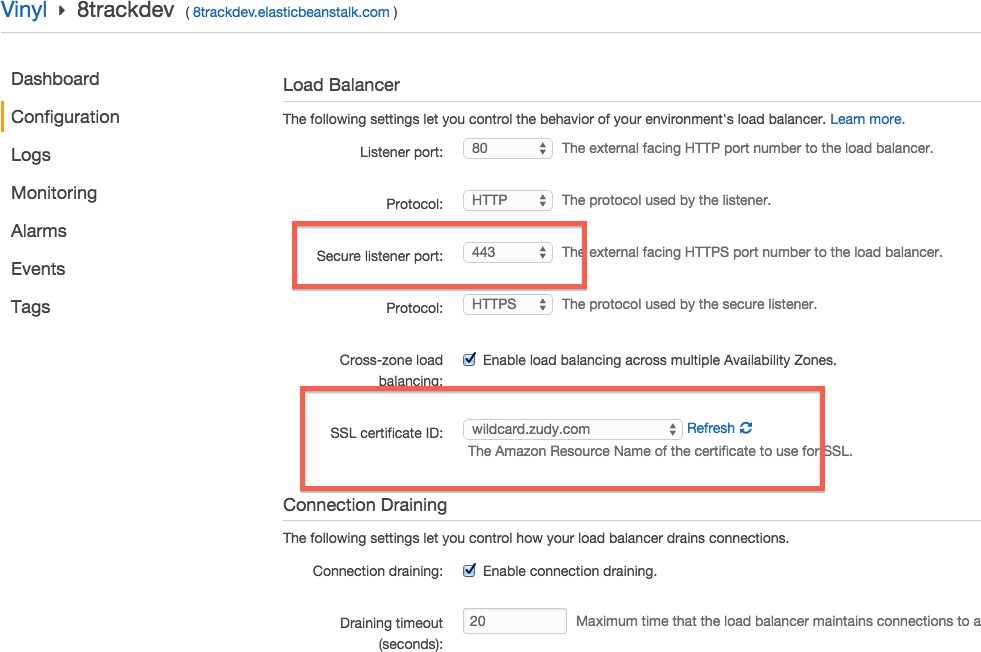
Wählen Sie das Zahnradsymbol neben Lastverteilung.
-
Setzen Sie den Sicheren Listener-Port auf 443.
-
Wählen Sie die zutreffende SSL-Zertifikat-ID aus.
-
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche Speichern: