Webhooks in Jitterbit App Builder
Overview
A webhook is an automated notification sent between applications when a specific event occurs. App Builder uses Webhooks to trigger specific actions in response to emails, text messages, or API calls.
For example, an application might email a user to approve or reject a transfer. If the user replies "approve", a webhook triggers the approval process; if they reply "reject", it triggers a rejection. This allows users to complete tasks directly from their inbox or messaging app without having to log back into the main application.
Create a webhook
Here is a summary of the steps needed to create a webhook:
Step 1: Add webhook in data servers
To set up a server, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the IDE.
-
Select IDE > Data Servers.
-
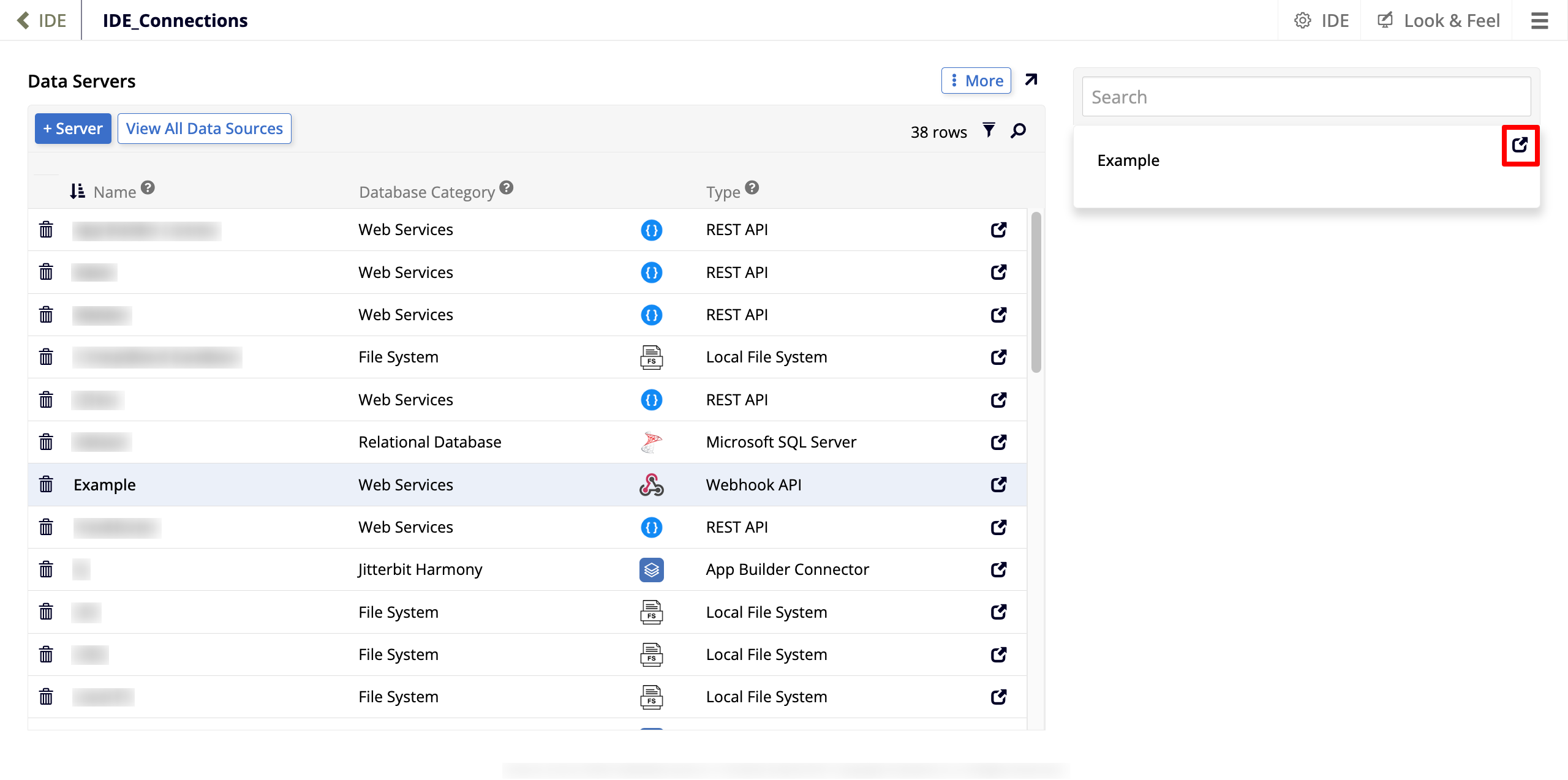
Click + Server. The Server dialog opens:
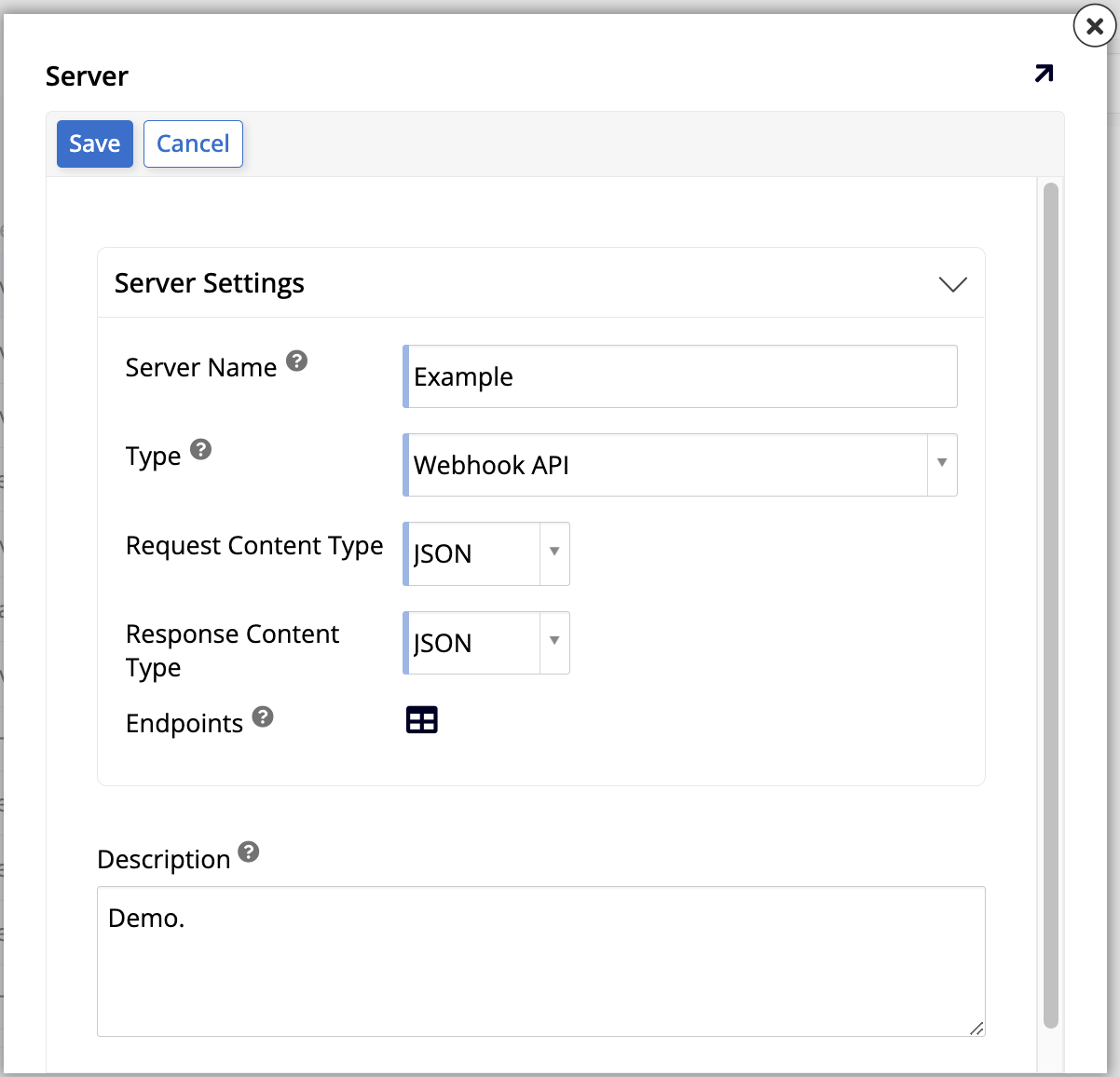
-
Set values for the following:
-
Server Name: Enter a name.
-
Type: Select Webhook API. This causes more options to be shown.
-
Request Content Type: Select JSON.
-
Response Content Type: Select JSON.
-
-
Click Save.
-
Exit the dialog.
-
To create an endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the list of servers, find the server you've just created and select it. Doing so lists the new server in the other panel on the screen.
-
Click the Open record icon:
-
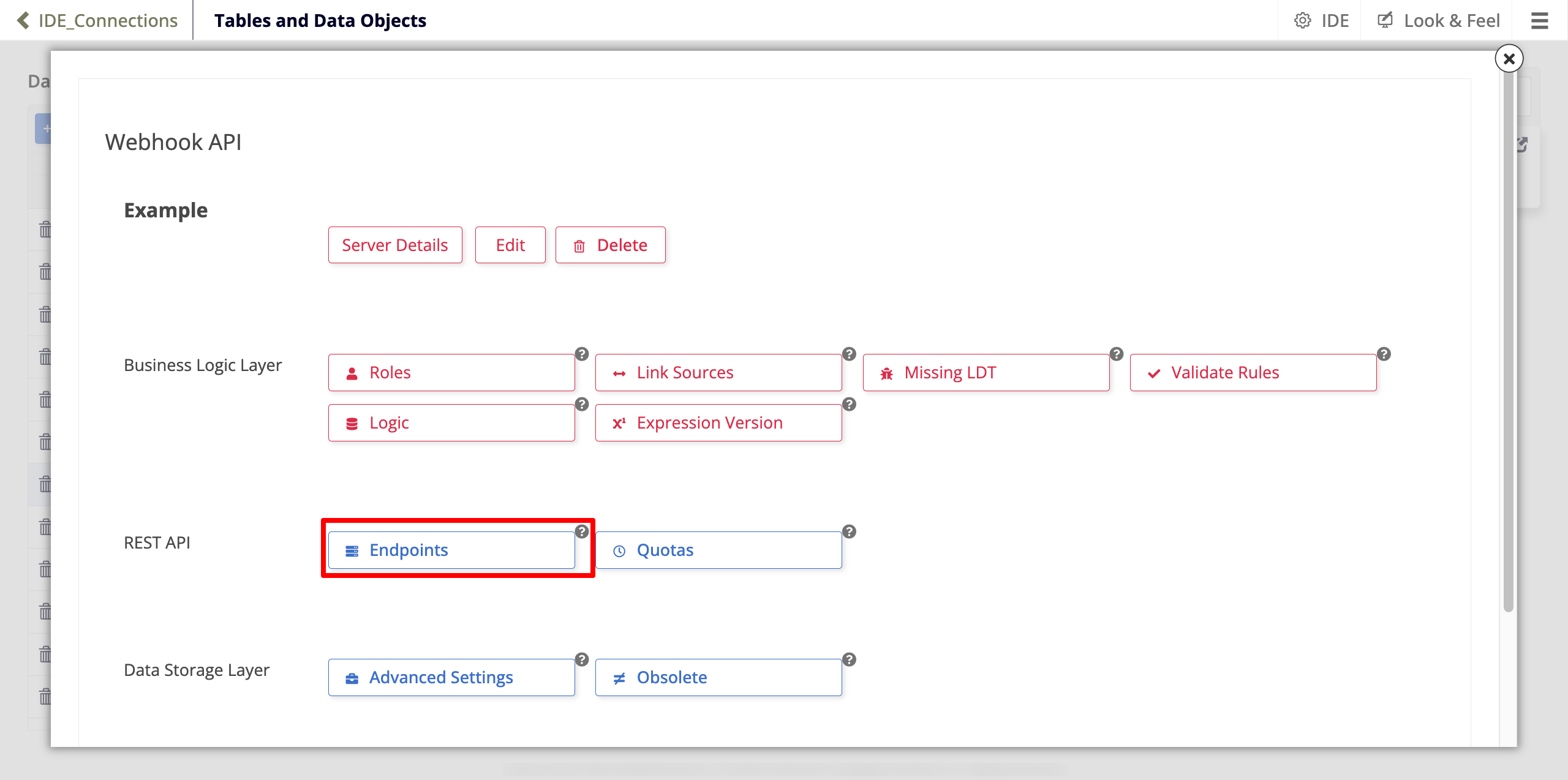
The Webhook API popup opens. In the REST API section, click Endpoints:
-
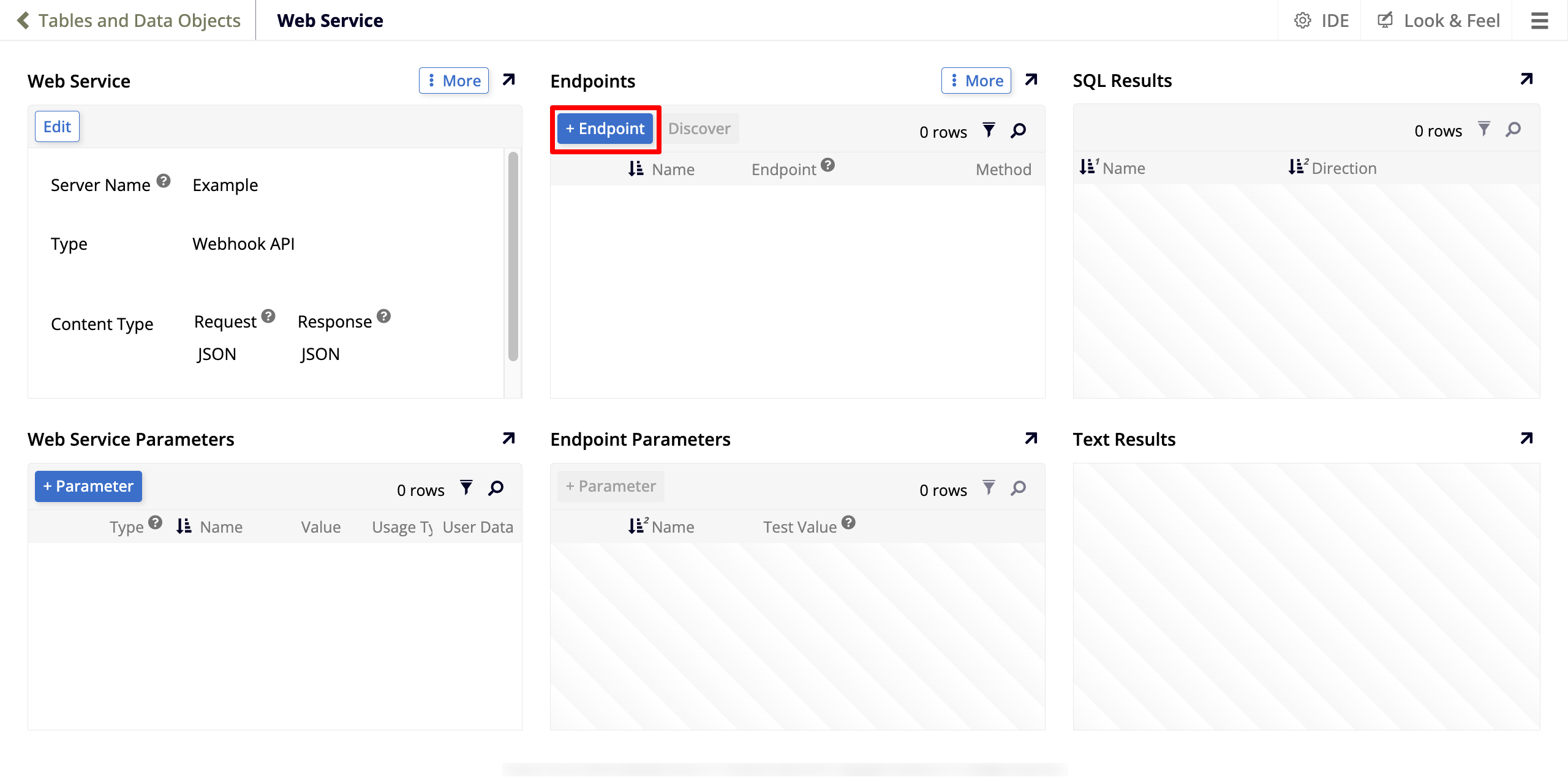
The Web Service page opens. In the Endpoints panel, click + Endpoint:
Set values for the following parameters:
-
Name: Pick a name for your endpoint.
-
Endpoint: You can leave this field empty.
-
Method: Select POST.
-
-
Click the checkmark icon to save.
To create parameters for your endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Endpoints panel, click Discover. The Endpoint dialog opens:
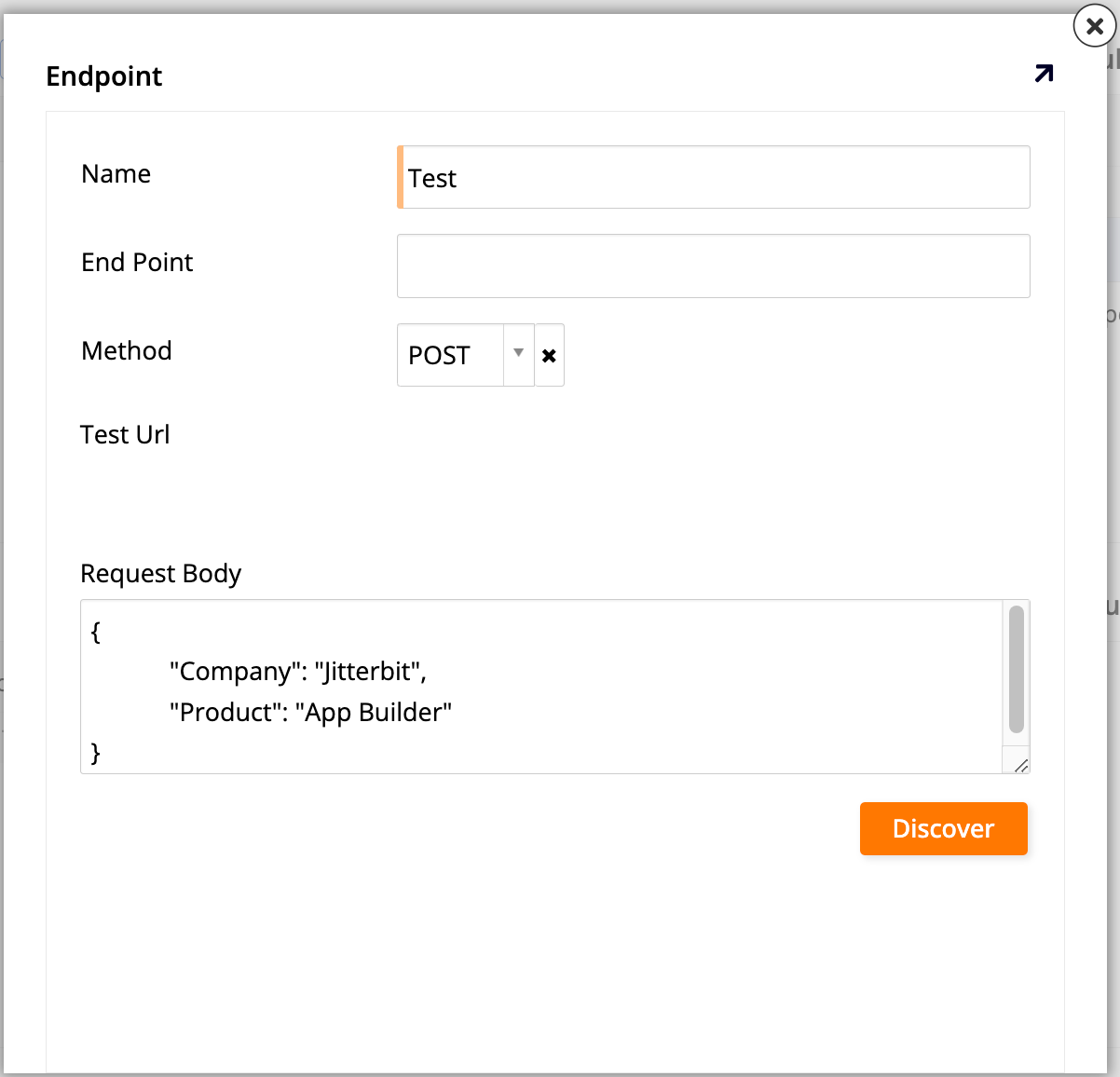
-
Set values for the following:
-
Name: This field is automatically filled with the name you've chosen for the endpoint.
-
End Point: You can leave this field empty.
-
Method: Select POST.
-
Request Body: If the webhook accepts a body (e.g., a POST using JSON or XML Request content type), provide a sample request body. For example:
{ "Company": "Jitterbit", "Product": "App Builder" }
-
-
Click Discover. App Builder automatically adds the endpoint parameters.
-
Step 2: Add webhook to your application
To add the webhook to your application, follow these steps:
-
Go to App Workbench > Data Sources.
-
Click + Source. A dialog opens.
-
Select Link to existing source.
-
Click Next.
-
Locate and select the REST Webhook API that you configured in Step 1 in the list.
-
Click the Link button.
-
Click Done.
Step 3: Create a webhook business rule
To create a business rule, follow these steps:
-
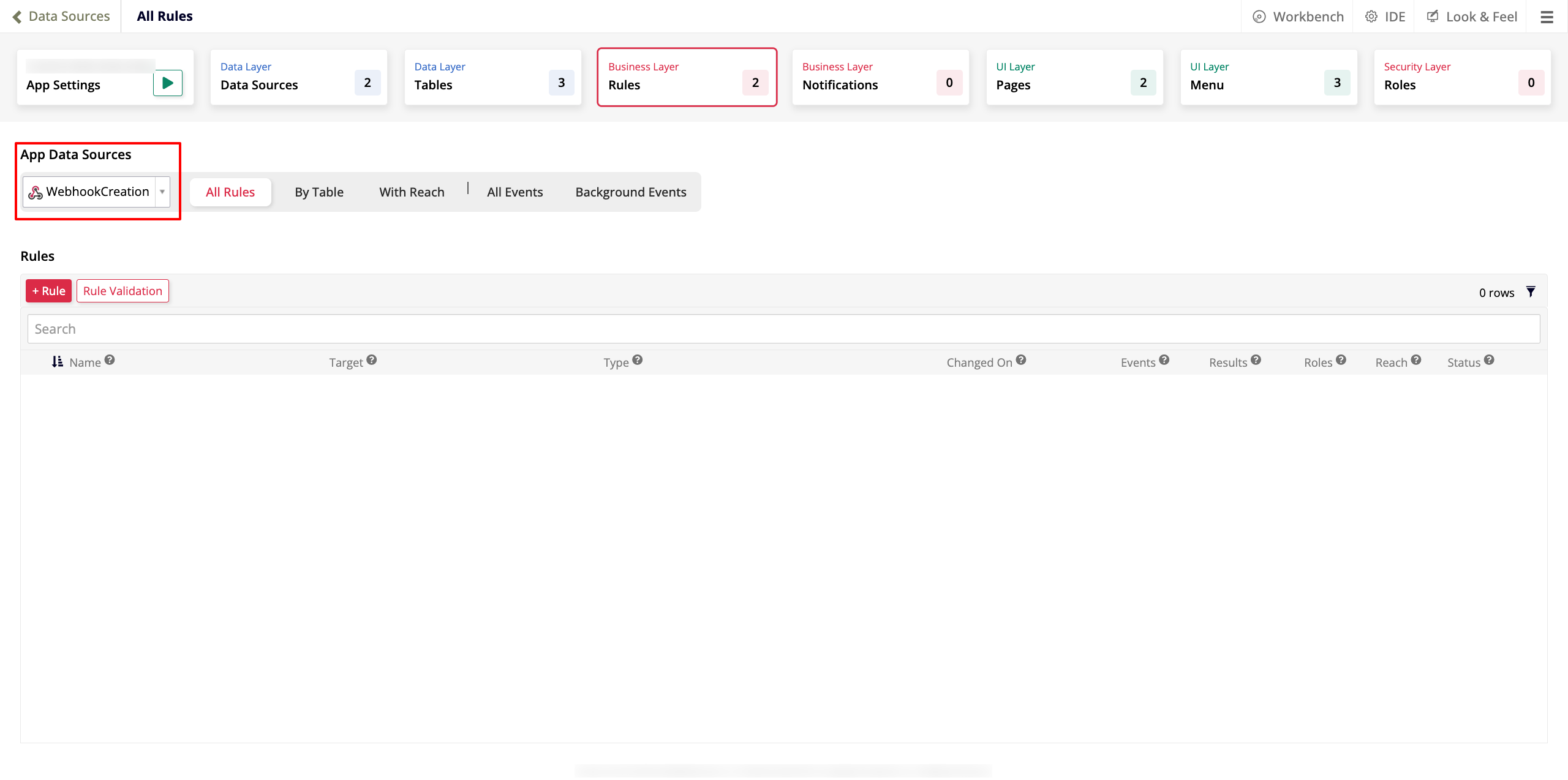
Go to App Workbench > Data Sources.
-
In the App Data Sources panel, select the webhook data source you've just created:
-
In the Rules panel, click + Rule. The Rule Builder opens.
-
Configure your new rule as follows:
-
Click Create. App Builder creates the rule and shows its edit screen.
-
In the Tables panel, click + Tables. A dialog opens.
-
Select the webhook endpoint by clicking its Add button. It appears on the Tables panel.
-
In the Tables panel, select all columns from the endpoint.
Step 4: Create an XP CRUD business rule
To create an XP CRUD business rule, follow these steps:
-
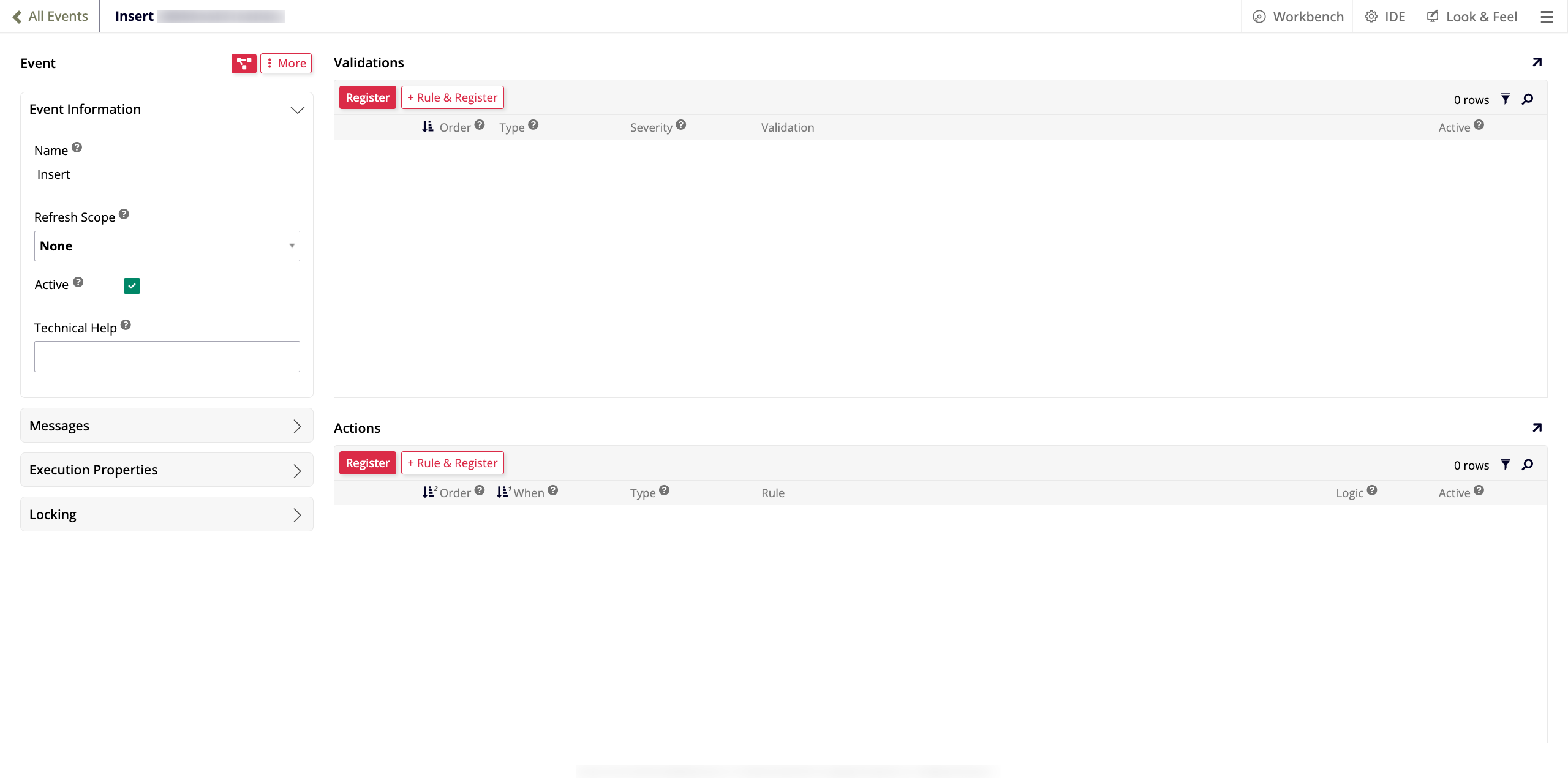
In the edit screen of the business rule you've created in Step 3, click Events in the Rule panel. The All Events dialog opens.
-
Double click the row with the Insert event. The Insert window opens:
-
In the Event Information panel, select Row Refresh in the Refresh Scope menu.
-
In the Actions panel, click + Rule & Register. A new instance of the Rule Builder opens. Configure it as follows:
-
Name: Give it a descriptive name, for example,
WebhookCreation_XP_CRUD. -
Purpose: Select XP CRUD.
-
Action: Select Insert.
-
Target Layer: Select Logic Layer.
-
Target: Select the business rule you created in Step 3.
-
-
Click Create. The new business rule is created and its edit screen appears.
-
In the Tables panel, click + Tables.
-
Select the endpoint you created in Step 1 by clicking its Add button. It will be shown on the Tables panel.
-
Select all of its columns.
-
Click Validate.
Step 5: Expose webhook
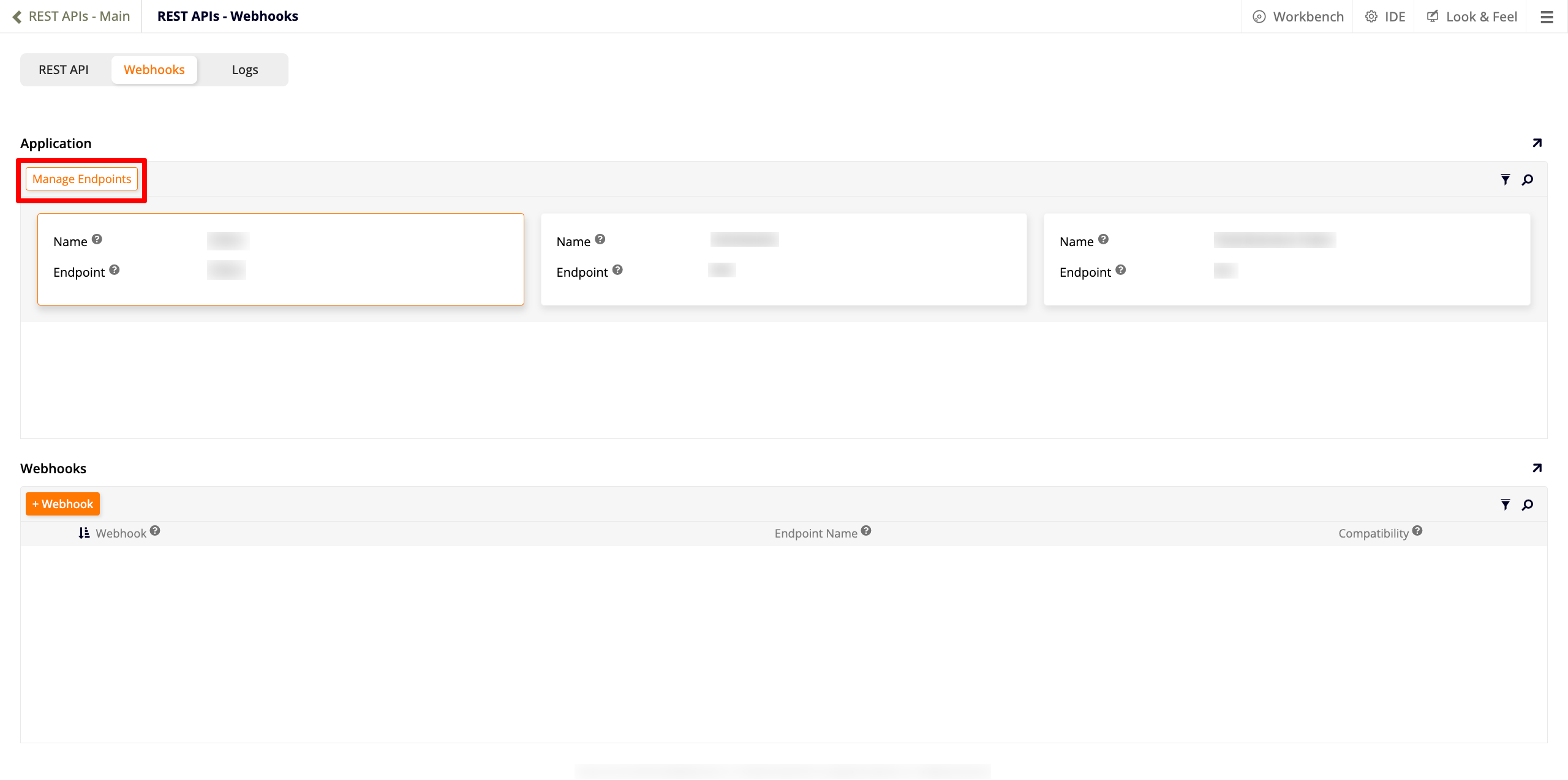
To create an endpoint for your application, follow these steps:
-
Select IDE > REST APIs.
-
Go to the Webhooks tab.
-
In the Application panel, click the Manage Endpoints button to open the Application Endpoints dialog:
-
Locate your application and click its pencil icon.
-
Enter a name for your endpoint, then click Proceed.
-
Exit the dialog. Your application will be listed with the others in the Application panel. Click its tile once to select it.
-
In the Webhooks panel, click + Webhook. The Webhook dialog opens:
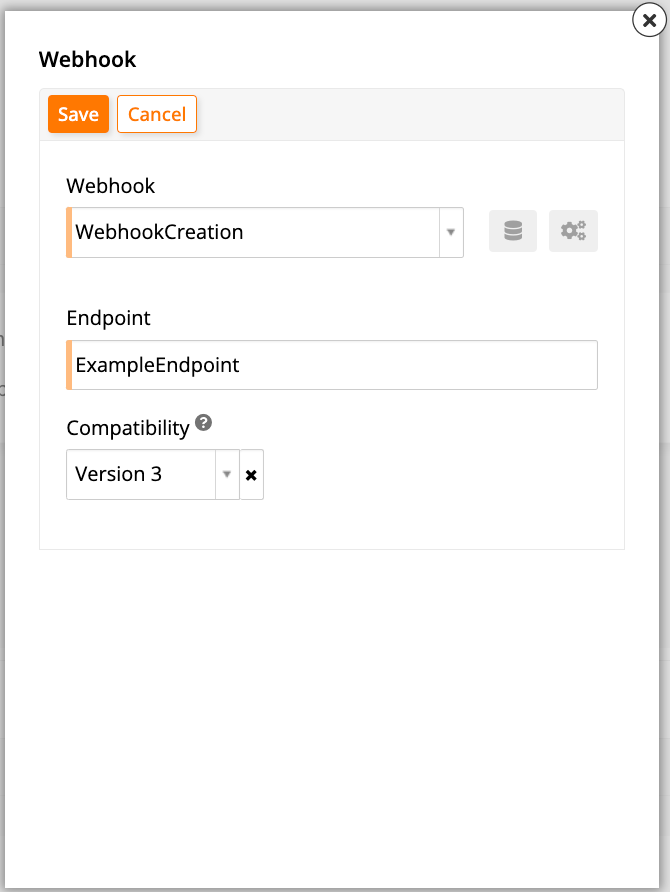
Configure it as follows:
-
Webhook: Select the webhook you've created.
-
Endpoint: Enter a descriptive name.
-
Compatibility: Leave the default option.
Note
Since App Builder 4.51, the Compatibility field provides these options:
-
Version 1: Use the original REST behavior—Insert events are not preceded by New events. (Default for endpoints created with App Builder 4.50 and earlier.)
-
Version 2: Use an improved REST behavior—New events and any default rules are invoked before Insert events. (Default for endpoints created with App Builder 4.51.)
-
Version 3: (Since App Builder 4.52.) Same as version 2, but where APIs return the logical value instead of the storage value. For example, boolean values are returned as
trueorfalseinstead of1or0. (Default for endpoints created with App Builder 4.52 and later.)
-
-
-
Click Save.
Step 6: Create an API key for a user to access this webhook
To create an API key (to allow a user access this webhook), follow these steps:
-
Select IDE > User Management.
-
In the Users panel, select a user that has administrator privileges and double click their row. The User dialog opens:
-
Click More > Keys. The Keys dialog opens.
-
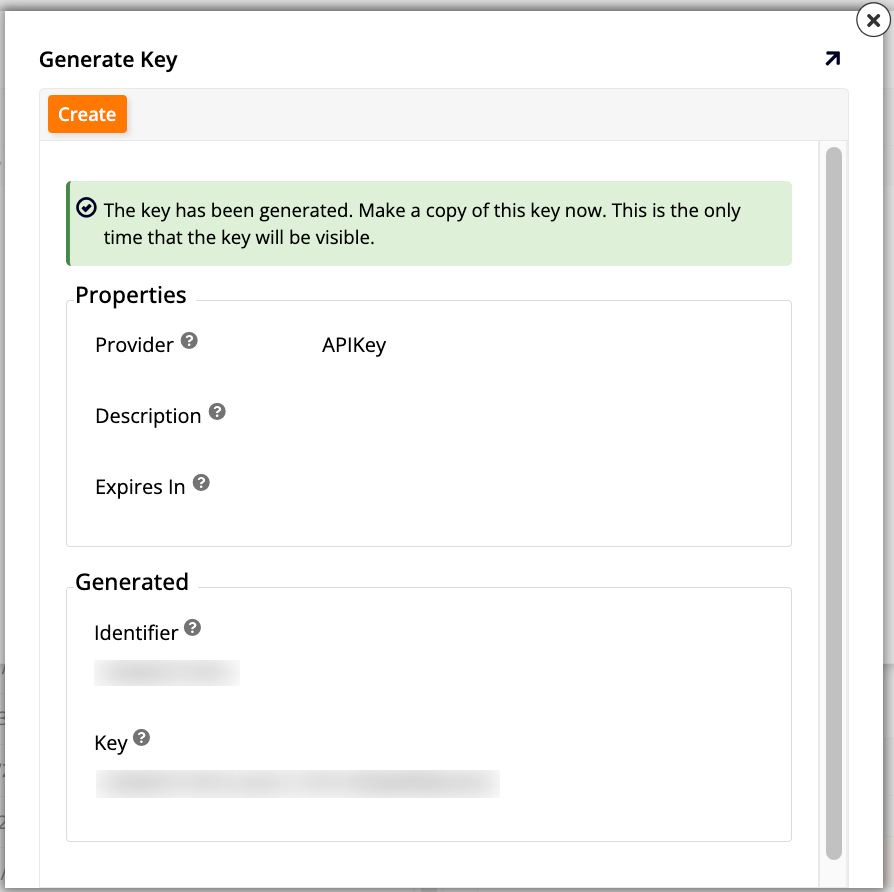
Click Create. The Generate Key dialog opens.
-
Configure the new key as follows:
-
Provider: Select APIKey.
-
Description: (Optional) Provide a brief description.
-
Expires In: (Optional) Enter a custom expiration time.
-
-
Click Save to create the API key.
Important
Note down the information as it cannot be shown again.
Step 7: Test
You should test your new webhook (using, for example, Postman, Insomnia, or similar tools). Send a POST API call with a body similar to the body sample used to create the parameters in Step 1. You should use basic authentication with the identifier and the key from Step 6 as the username and password.
For testing, use the link: https://<url>/webhook/v1/<application-endpoint>/<endpoint>.
When no authentication is required, instead of configuring an x-api-key in the header, you can adjust the URL to one of the following options:
-
https://{{user's identifier from Step 6}}:{{user's key from Step 6}}@{{url from Step 7}}(to be used if the provider is HTTP basic auth with no parameters)Caution
The HTTP basic method described above requires the Authorization header to be included in the received payload. To bypass this, use the API Key method instead.
-
https://{{url from step7}}?apiKey={{user's key from Step 6}}(to be used if the provider is API Key and the Properties include HttpHeaderName 'X-API-Key')